The more comprehensive and competent the diagnosis of prostatitis, the more effective the subsequent treatment will be. The doctor’s formal treatment may result in long-term ineffective treatment. Its task is to identify the inflammation of the prostate and all the factors that cause prostatitis.
How does a doctor diagnose prostatitis
Prostatitis is diagnosed by a urologist or andrologist. After talking with the patient, the doctor will prescribe the necessary examinations: first a set of standard examinations (blood, urine, prostate secretion, rectal examination), and then, if instructed, will use more detailed high-tech methods: CT, MRI, ultrasound.
Make memories
During the initial consultation, the doctor will ask the following questions:
- The duration of intercourse (if it becomes shorter, under what circumstances);
- Discomfort in the groin after staying still for a long time, drinking alcohol or hypothermia;
- Frequency and speed of urination (what's the difficulty, intermittent jet flow, do you often get up at night to go to the bathroom)?
- The quality of orgasm (still bright or fuzzy, painful ejaculation).
The more details the patient remembers, the more complete the clinical picture made by the doctor.
Differential diagnosis
The symptoms of prostatitis are similar to the symptoms of many other diseases:
- Cystitis (spasm during urination, lower abdomen pain).
- Adenoma (dysuria, heaviness in the groin).
- Prostate cancer (blood urine, problems with urination).
- Rectal lesions: hemorrhoids, paracolitis (inflammation), anal fissure, nephritis (ulcerative colitis).
Other diagnostic methods and their principles of use are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Differential diagnosis of prostatitis
| Disease | Risk Group | Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperplasia | Male over 45 years old, without urethritis, catheterization, history of bladder and urethral trauma (may explain pain, blood in urine) | Ultrasound and digital examination of prostate |
| Prostatitis | Most of them are young people with recent fever and hypothermia. In these histories, there are no predisposing factors (same as hyperplasia) | Ultrasound, complete blood count (CBC), digital prostate examination |
| Prostate cancer | Men over 45 years old, no history of predisposing factors | Prostate ultrasound, PSA analysis, digital examination |
If necessary, other professional doctors can also participate in the diagnosis: rectal doctor, neurologist, vertebral surgeon. The latter two experts determined the causes of pain related to spinal structure invasion and nerve ending invasion.
Rectal Palpation
Digital rectal examination is the most convenient and useful way to check the status of the prostate. During the operation, the doctor will pay attention to the following parameters of its structure:
- volume;
- density;
- Surface roughness;
- Homogeneity (homogeneous organization);
- Border (clear outline);
- Keep the isthmus (longitudinal suture between the lobes).
In prostatitis, the glands are enlarged (possibly asymmetric) due to edema, the consistency is elastic, the longitudinal grooves (sutures) cannot be touched, and the patient may feel pain when touching.
In order to clearly understand this type of diagnosis, it is necessarypreparation:
- Don't ejaculate the day before, don't drink alcohol, avoid strenuous exercise, hypothermia and overheating.
- Do not ride a bicycle for a day, do not use a rowing machine (do not hurt or massage the prostate in this way).
- Before going to the doctor, clean the rectal ampoule with an enema (microenema can be used).
You can feel the prostate at a depth of 3-5 cm from the anus. The doctor uses sterile gloves to perform the operation and lubricates the fingers with gel. The patient has his knee bent, lying on his side or standing on his elbow.
Laboratory method
Laboratory methods for diagnosing prostate inflammation include biological materials that investigate the presence of pathogens.
Blood
According to the results of routine and biochemical blood tests (capillaries taken from the fingers), prostatitis can be suspected at an early stage. Analyze on an empty stomach in the morning. You should quit smoking one hour before the operation.
Important indicators:
- White blood cells (blood cells, the number of which increases as the immunity against the background of inflammation decreases). Usually 4-9×10 ^ 9 units;
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). The normal value is about 5 units, an increase indicates inflammation or tumor process;
- Lymphocytes. Generally, their percentage of the total volume of blood cells is 18 to 40 units. Overdose means infection.
Men over 40 years of age are required to have a PSA test-a tumor marker whose value exceeds this value to indicate chronic prostatitis or prostate cancer.Specification-Less than 4 ng / ml, and -5. 53 ng / ml after 50 years.
Urine
The urethra passes through the prostate (the prostate part of the urethra), so when the glands become inflamed, the urine changes its color and consistency. In order to diagnose prostatitis, three types of analysis are performed:
- General-determination of physical and chemical parameters. Signs of prostate inflammation: cloudy, whitish, alkaline, protein, white blood cells, purulent filaments, and sometimes foaming or oozing. For calculous prostatitis, phosphate is found.
- Cytology-check whether there are pathologically changed cells. The presence of red blood cells and epithelium may indicate tumor progression.
- Bacteriology-identification of traces of pathogenic microorganism activity. For this purpose, the tank is used to spread sediment on the nutrient medium. If there are bacteria and fungi, they begin to reproduce actively after a period of time. E. coli often causes prostatitis.
Before passing urine, avoid salty and spicy foods, and avoid alcohol and coloring products (beets, coffee). The analysis was performed in the morning on an empty stomach.For prostatitis, use the three-cup examination:The patient urinates alternately with each cup; the result is the first part, the middle part and the last part. This method allows you to determine the location of inflammation: urethra, prostate, bladder. The four-cup method has more reference value. Obtain a final urine sample after prostate massage to obtain its secretions.
Prostate secrets and sperm
The juice produced by the prostate is a valuable diagnostic material. Prepare the fence in the same way as the digital rectal exam. In order to keep the secret sufficiently substantial, you should avoid sexual intercourse for three to five days.
Method of checking prostate secretion:
- microscope;
- Sowing;
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction).
PCR is the most accurate method. To process biological materials, special enzymes are used to increase the number of DNA and RNA fragments of pathogens. In order to conduct research, a special equipment-a silencer is needed. The most accurate real-time PCR. The results are ready within an hour.
The inflammation of the prostate is represented by the presence of amyloid, staphylococcus, streptococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and epithelial cells (more than three units in the field of view) in its juice. The number of lipid particles decreases and the number of white blood cells increases.
Thesperm photo of prostatitisis an additional analysis. Against the background of inflammation of the prostate, the sperm turns yellowish or brown, its viscosity increases (liquefies for a long time), and pathogenic bacteria are present. In chronic prostatitis, glandular epithelial cells, amyloids and mucus are found.
Urethral swab
Compared with diagnosing secretions, urethral swabs (scratches) are a less informative method for diagnosing prostatitis.Used for hemorrhoids, increased inflammation, and calcification in the prostate and the latter cannot be obtainedThe process of obtaining the material was very fast, but it was very uncomfortable: the doctor dipped the brush into the urethra, and the urethra captured some of the cells and microorganisms covering the urethra. The biological material is then checked by PCR, which allows you to determine the presence of any number of pathogens. The cause of prostatitis may be a genital infection: Chlamydia, Trichomonas, Mycoplasma.
Before performing the analysis, you should refuse sexual intercourse within a day. In the morning, only perform external hygiene procedures on the penis (do not pour anything into the urethra) and do not urinate for two hours.
Instrument method
The instrument diagnostic method allows you to confirm and supplement the results of laboratory tests.
Ultrasound and TRUS
Ultrasound examination of the prostate can visualize its structure, contour, and the nature of tissue changes. In the case of prostatitis, transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) is considered the most useful information: the doctor inserts the probe into the rectum. Prepare for surgery in the same way as palpating glands. An abdominal ultrasound (through the abdomen) is more comfortable for men, but the prostate is not completely visible due to the bladder.
With inflammation of the prostate, its structure is uneven, the outline is blurred, there may be fibrotic lesions (overgrowth of connective tissue), scars. The prostate enlarges and the grooves between its leaves become smooth.
MRI, PET and CT
If the ultrasound has reason to suspect the presence of a tumor, the doctor will order a CT (computed tomography) or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to clarify the image. The latter type of research is more accurate, but also more expensive. The procedures are painless, and in terms of information content, they can replace biopsies (crushing tissue fragments).
CT and MRI show in detail the structure of the prostate: stones, cysts, tumors, inflammatory foci, and structural abnormalities. In order to obtain a clearer image, the contrast agent is injected into the vein in advance (not for men with renal failure). For this procedure, use an appropriate type of tomography scanner and rectal sensor.
PET-Positron emission CT. Allows you to analyze the condition of the prostate at the cellular and molecular level. It not only determines the existence and size of the tumor, but also the speed and quality of the metabolic processes that occur within it.
About preparations:The rectum should be emptied. Do not eat for five hours before the operation.
Diagnostic features of certain types of prostatitis
Acute bacterial (infectious) prostatitis is diagnosed based on the patient’s chief complaint, urinalysis, ultrasound examination, and urethral smear.For active inflammation, the gland will be painful, and rectal intervention is not allowed. In extreme cases, please check your fingers carefully.
Laboratory data for diagnosing acute prostatitis is not particularly useful. Urine culture may be desirable, but not necessary. For active inflammation, there is no time to wait for the results. To relieve symptoms, a broad-spectrum drug is used for antibacterial treatment.
Chronic prostatitis does not actually manifest itself in any way. Therefore, its detection requires a complete set of laboratory, physical, and instrumental methods. It may be necessary to determine the patient's immune and neurological status.
Palpation of the glands, urine and prostate secretions is essential. The presence of more than 10 white blood cells in the visual field indicates inflammation. If the bacterial culture does not increase the infectious microflora in the context of an increase in the number of white blood cells, an analysis of genital infection is required.
has the bacterial nature of inflammation in urine and prostate fluid, so a large number of pathogens have been found. An undeniable microbiological sign of chronic inflammation: the number of microorganisms per milliliter (CFU) exceeds 104. Some of them have dozens of numbers, so they are present in amounts ranging from 10 to 102 per milliliter, which may indicate prostatitis.
This phenomenon does not exist in non-bacterial (non-infectious) inflammation, but experts recommend a more in-depth analysis in this case: puncture the prostate to extract pathogens living in closed prostate channels. At the same time, the bacterial culture is sterile, but eventually pathogens are still found. Usually, it is a type of E. coli.
Ultrasound does not always show chronic inflammation. In addition to the above methods, doctors can also prescribe a urine flow meter-using a special sensor to measure the flow rate of urine.
Typical complications
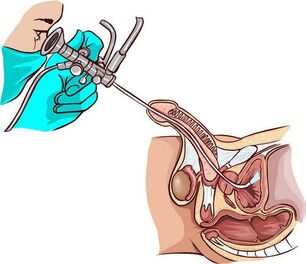
For long-term chronic prostatitis with signs of colitis (seminal vesiculitis next to the prostate), use urethroscopy-a visual inspection of the canal with endoscopic equipment. It helps to identify urethral stricture, damage to the structure of the urethra, the condition of the prostatic discharge tube (mucus, pus, thickening) and seminal vesicle nodules.
Interpretation of results (prostatitis staging defined by semen nodule status):
- First of all: the seed nodules are red, edema, and bleeding. The same pattern was observed in the back of the urethra.
- Second: Periodic increases and decreases in redness and swelling are characteristic.
- Third: Scarring changes occur in the nodules and urethral tissue, so the lumen of the ureter may become narrow (stenosis).
Cystitis is also the partner of chronic prostatitis. Ultrasound and cystoscopy can detect inflammation of the bladder wall. During the study, pathological changes in the mucosa were identified, especially in the neck. The state of the bladder in the context of chronic prostatitis (sclerosis of the prostate):
- Triangular scar deformity of the bladder.
- Dilation of the ureteral orifice.
- Neck narrows.
In the case of lower abdominal pain and frequent urination, cystoscopy has been prescribed in the final stage of the examination.
The most difficult to diagnose is chronic bacterial prostatitis, accompanied by pelvic pain, of unknown origin. In such patients, doctors first conduct research to rule out cystitis and neuropsychiatric pathology.
How to diagnose prostatitis at home
A person can suspect acute prostatitis through the following signs:
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen and groin (between the testicles and anus);
- Increased body temperature;
- Pain when urinating (such as cystitis);
- Early and painful ejaculation.
The same symptoms can occur during the exacerbation of chronic prostatitis caused by hypothermia or alcohol consumption. The periodic appearance of blood in the urine, dull pain in the perineum (especially in a static position), difficulty urinating, and worsening erections may indicate the development of this pathological form. These signs are the reason to contact the urologist.
Conclusion
The longer the prostatitis process lasts, the more difficult it is to treat, so you should not delay diagnosis. In government agencies, most procedures and follow-up treatments are free.

























